The BoP or balance of payments records the undertakings or transactions of commodities, assets, and services between the citizens of a nation with the rest of the world for a stated time frame frequently every year. There are two main accounts in the BoP.
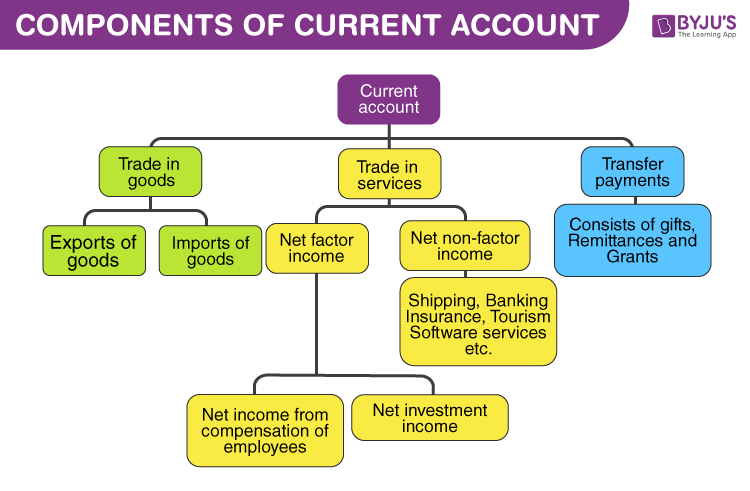
The c urrent account is a record of businesses in commodities, transfer payments, and services. Trade-in commodities comprise the exports and imports of commodities. Trade-in services comprise factor income and non-factor income transactions or undertakings.
Transfer payments are the receipts that the citizens of a nation get for free’, without having to provide any commodities or services in return. They consist of remittances, grants, and gifts. They could be provided by the government or by private residents living abroad.

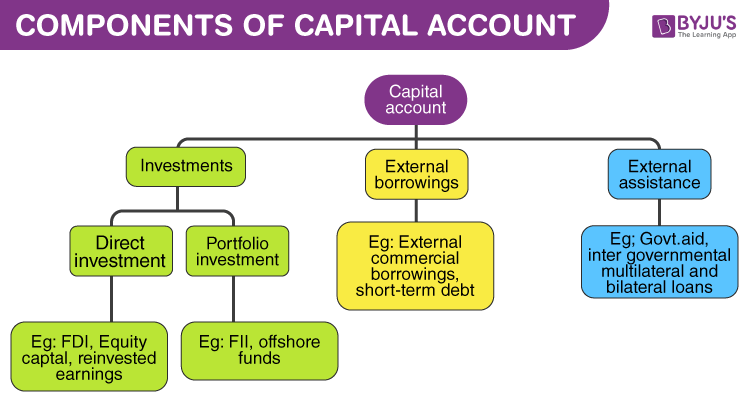
The c apital account records all the international undertakings of assets. An asset is any one of the types in which wealth can be held. For instance, stocks, bonds, government debt, money, etc. The purchase of assets is a debit on the capital account. If an Indian purchases a UK car company, it enters the capital account undertakings as a debit (as foreign exchange is going out of India).
On the other hand, the sale of assets, like the sale of the share of an Indian company to a Japanese customer, is a credit on the capital account. These items are foreign direct investments (FDIs), foreign institutional investments (FIIs), assistance, and external borrowings.
| 1 MARK QUESTIONS |
| Q 1. What is the balance of payment account of a country record? |
| Answer: |
(i) Current account
| Q 5. Define current account.. |
| Answer: |
Components of current account are:
a) Import and export of goods
b) Import and export of services
c) Unilateral transfers
The above mentioned is the concept that is explained in detail about The Balance of Payments for the Class 12 students. To know more, stay tuned to BYJU’S.